cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage (cloud storage) and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each location being a data center. Cloud computing relies on sharing of resources to achieve coherence clarification needed and economies of scale, typically using a “pay-as-you-go” model which can help in reducing capital expenses but may also lead to unexpected operating expenses for unaware users.
Goals Of Cloud Computing
The goal of cloud computing is to allow users to take benefit from all of these technologies, without the need for deep knowledge about or expertise with each one of them. The cloud aims to cut costs and helps the users focus on their core business instead of being impeded by IT obstacles. The main enabling technology for cloud computing is Virtualization software separates a physical computing device into one or more “virtual” devices, each of which can be easily used and managed to perform computing tasks.
With operating-system-level virtualization essentially creating a scalable system of multiple independent computing devices, idle computing resources can be allocated and used more efficiently. Virtualization provides the agility required to speed up IT operations and reduces costs by increasing infrastructure utilization. Autonomic computing automates the process through which the user can provision resources on-demand. By minimizing user involvement, automation speeds up the process, reduces labor costs, and reduces the possibility of human errors.
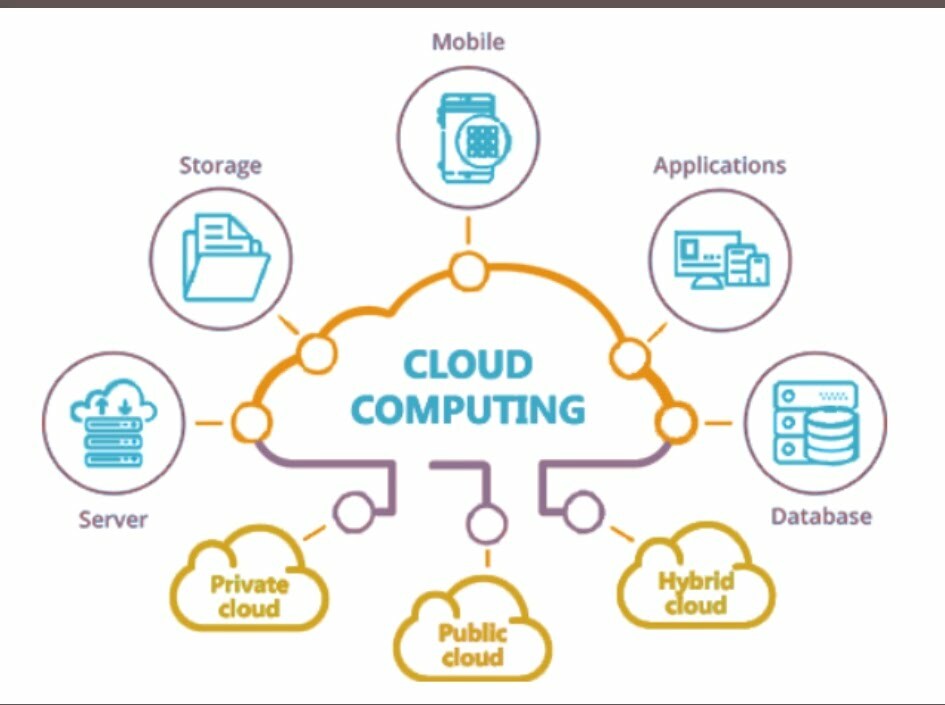
Cloud Computing Characteristics-
- An on-demand self-service-A consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider.
- Broad network access-. Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and workstations).
- Resource pooling.- The provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model, with different physical and virtual resources dynamically assigned and reassigned according to consumer demand.
- Rapid elasticity- Capabilities can be elastically provisioned and released, in some cases automatically, to scale rapidly outward and inward commensurate with demand. To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear unlimited and can be appropriated in any quantity at any time.
- Measured service-Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service (e.g., storage, processing, bandwidth, and active user accounts). Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported, providing transparency for both the provider and consumer of the utilized service
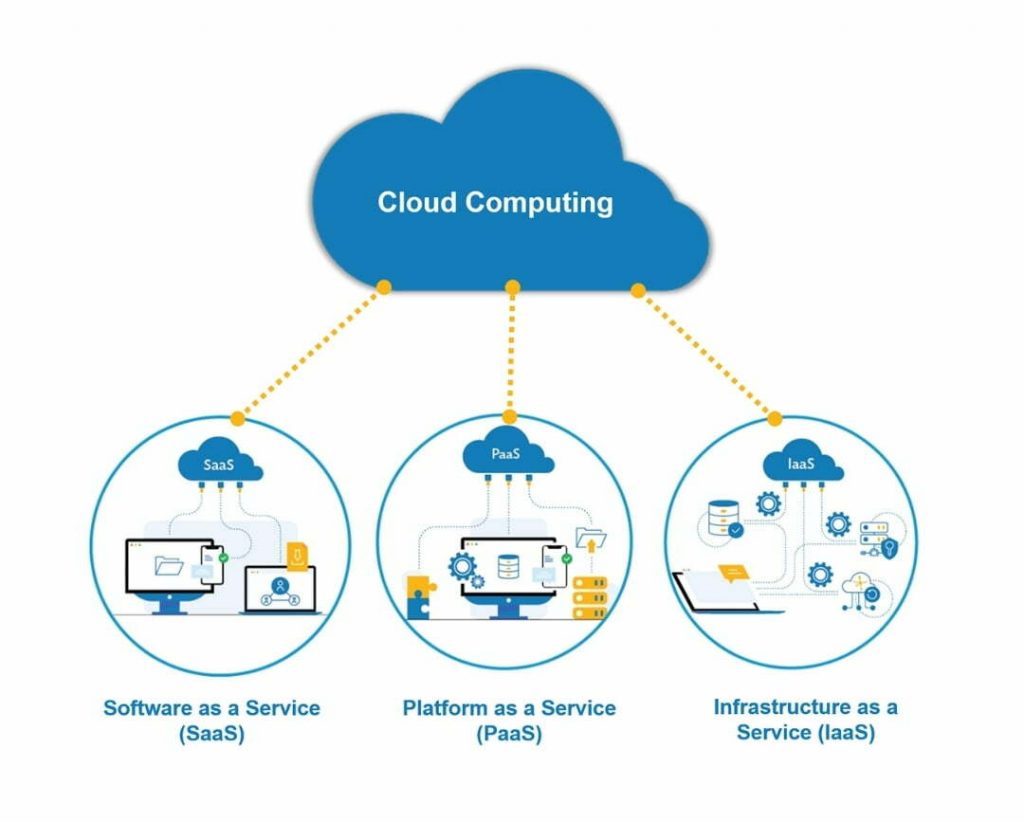
Types Of Cloud Computing Services-
Cloud computing can be separated into three general service delivery categories or forms of cloud computing:
- IaaS. IaaS providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), supply a virtual server instance and storage, as well as application programming interfaces (APIs) that let users migrate workloads to a virtual machine (VM).
Users have an allocated storage capacity and can start, stop, access, and configure the VM and storage as desired.
IaaS providers offer small, medium, large, extra-large, and memory- or compute-optimized instances.
In addition to enabling customization of instances, for various workload needs. The IaaS cloud model is closest to a remote data center for business users.
2..PaaS. In the PaaS model, cloud providers host development tools on their infrastructures. Users access these tools over the internet using APIs, web portals, or gateway software. PaaS is used for general software development, and many PaaS providers host the software after it’s developed. Common PaaS products include Salesforce’s Lightning Platform, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Google App Engine.
3. SaaS. SaaS is a distribution model that delivers software applications over the internet; these applications are often called web services. Users can access SaaS applications and services from any location using a computer or mobile device that has internet access. In the SaaS model, users gain access to application software and databases. One common example of a SaaS application is Microsoft 365 for productivity and email services.
Cloud Architecture
The systems architecture of the software systems involved in the delivery of cloud computing. Typically involves multiple cloud components communicating with each other over a loose coupling mechanism such as a messaging queue. Elastic provision implies intelligence in the use of tight or loose coupling as applied to mechanisms such as these and others.

Cloud Engineering
Cloud Engineering is the application of engineering disciplines of cloud computing. It brings a systematic approach to the high-level concerns of commercialization, and standardization. governance in conceiving, developing, operating, and maintaining cloud computing systems.
Cloud Computing is a multidisciplinary method encompassing contributions from diverse areas. Such as systems, software, web, performance, information technology engineering, security, platform, risk, and quality engineering.
https://www.thecyberdelta.com/object-oriented-programming/amp/









